
MVP software development enables startups to launch faster, validate real demand, and reduce costs. At EnactOn Technologies, we have delivered 350+ solutions across 65 countries, giving us direct insight into what makes MVPs succeed. The lesson is clear: disciplined execution, validated learning, and user-centered design consistently outperform traditional methods.
Key Statistics on MVP Success: Why the Numbers Tell the Real Story
Industry research confirms that 72% of startups use MVP Software Development. Among them, 67% succeed, compared to 33% with traditional builds. This makes the MVP software development lifecycle one of the most reliable paths to validation.
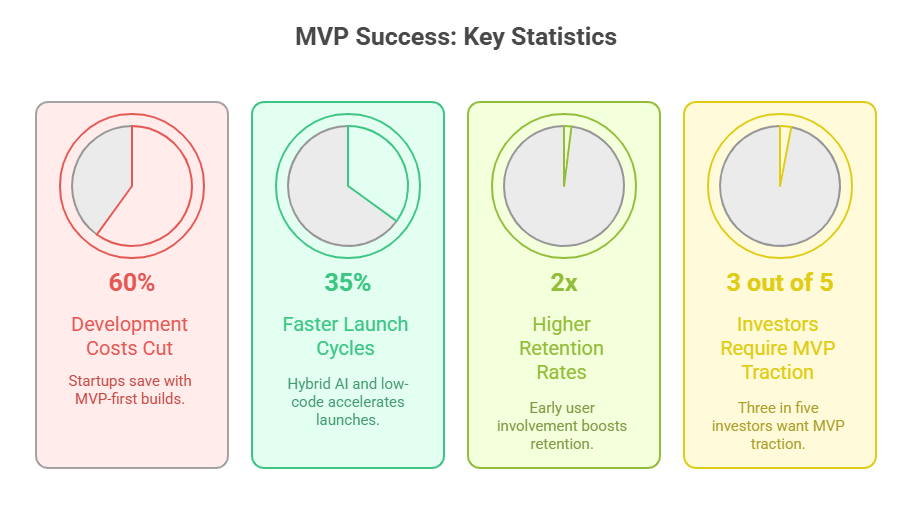
Recent 2024–2025 studies go deeper:
● Startups cut 60% of development costs when using MVP-first builds (CB Insights).
● Hybrid AI + low-code methods create 35% faster launch cycles.
● Early user involvement leads to 2x higher retention rates.
● 3 out of 5 investors require MVP traction before considering funding.
These numbers highlight how MVPs reduce financial risk while building market confidence and trust among both users and investors.
The Psychology Behind MVP Software Success: Why Users Fall in Love Early
MVPs work because they align with how people behave when they discover new products.
● Immediate value delivery matters most. Even limited features that solve urgent problems create attachment. This explains why the “minimum lovable product” effect drives early loyalty.
● Feedback creates ownership. When user suggestions feed into the MVP requirements document, they feel like contributors, not passive customers. This emotional connection builds advocacy.
● Scarcity amplifies appeal. Exclusive access to limited features makes early adopters feel special. This word-of-mouth effect reduces acquisition costs significantly.
These psychological triggers explain why even minimum viable product document examples with stripped-down functionality can attract loyal communities.
Industry Practices Reshaping MVP Development: How Teams Build Smarter Today
The landscape of SaaS MVP development has shifted toward speed, automation, and validation-driven iteration.
● AI development tools now reduce coding and bug detection time by 20–25%.
● Low-code and no-code platforms allow faster prototyping, letting non-technical teams test ideas.
● Hybrid approaches combine no-code for validation and custom builds for scaling.
● Data-first culture ensures teams track 20+ KPIs, from churn to adoption, instead of relying on assumptions.
It’s not just startups. Enterprises like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon run MVP tests before global rollouts. Fintech giants like Stripe validate products through limited-release MVPs before scaling internationally. This proves the MVP software development lifecycle is as crucial for corporates as it is for startups.
5 MVP Software That Transformed Their Industries
1. Notion: How Modular Workflows Created a New Category
Launched in 2016, rebuilt in 2018. Notion’s early MVP focused on notes and databases but struggled technically. By relocating to Kyoto, the team lowered costs and focused on rebuilding.
Their second iteration introduced modular workflows shaped by requirements. Users could design their own systems instead of waiting for every feature.
● 30M+ users worldwide
● $567M ARR in 2023
● Valuation of $10B+
Notion’s story shows how MVP discipline can create entirely new categories rather than compete in crowded ones.
2. Discord: When Gaming Chat Became Global Community Software
Launched in 2013. The MVP was built around low-latency voice calls and lightweight text messaging. This solved gamers’ frustrations with unreliable platforms like Skype.
Through testing, the team discovered non-gamers using Discord for classrooms, clubs, and communities. Insights from minimum viable product document examples shaped this pivot.
● 300M+ registered users by 2022
● 47% engagement spike during early 2020
● Valued at $15B+
Discord proves that MVPs often uncover bigger adjacent markets than founders initially expect.
3. Slack: From Failed Game to the World’s Office Chat Tool
Built in 2013 as an internal communication tool for a gaming project called “Glitch.” The MVP offered just channels, direct messages, and file sharing.
Its simplicity set it apart from complex enterprise software. Slack grew by monitoring user behavior, expanding features only when engagement data supported them. This SaaS MVP development approach ensured usability stayed intact.
● 18M daily users by 2022
● Used by 750,000+ companies
● Fastest-growing B2B app of its era
Slack shows how an MVP born from failure can still become a market leader.
4. Figma: Redefining Design Through Browser Collaboration
Launched in 2015. The MVP prioritized real-time editing inside a browser, challenging the belief that professional design required desktop apps.
Though feature-light, Figma’s MVP solved collaboration pain points Adobe could not. The MVP software development lifecycle emphasized innovation over parity, creating new workflows.
● Acquired by Adobe for $20B in 2022
● Used by 4M+ designers globally
● Now dominant in collaborative design
Figma proves MVPs can win by rethinking delivery models, not just features.
5. Obsidian: Winning a Niche with Privacy and Local Control
Launched in 2020. The MVP allowed markdown-based notes with local storage and bi-directional links. Privacy-conscious users embraced this, avoiding cloud-only rivals.
Their approach prioritized extensibility. Plugins, built by the community, expanded functionality organically.
● Over 1M+ users in 3 years
● Thriving plugin ecosystem
● Strong loyalty within niche markets
Obsidian shows that even focused minimum viable product document examples can succeed when they meet specific, underserved needs.
Why These Approaches Work: Lessons Every Founder Can Apply
Across all five cases, three shared principles appear consistently:
● MVPs solve a defined problem for a focused audience.
● MVPs launch core features only, iterating based on real use.
● MVPs design scalable architectures that support growth without rebuilding.
According to Gartner’s 2025 report, companies using MVP frameworks cut costs by 60% and speed launches by 35%. These gains compound into long-term competitive advantage.
How to Write a Strong MVP Requirements Document
An MVP requirements document defines the foundation for successful product launches. It ensures that teams stay aligned on the problem being solved, the scope of features, and the metrics for success. Without it, the MVP software development lifecycle risks drifting off-course.
Key Elements of an MVP Requirements Document
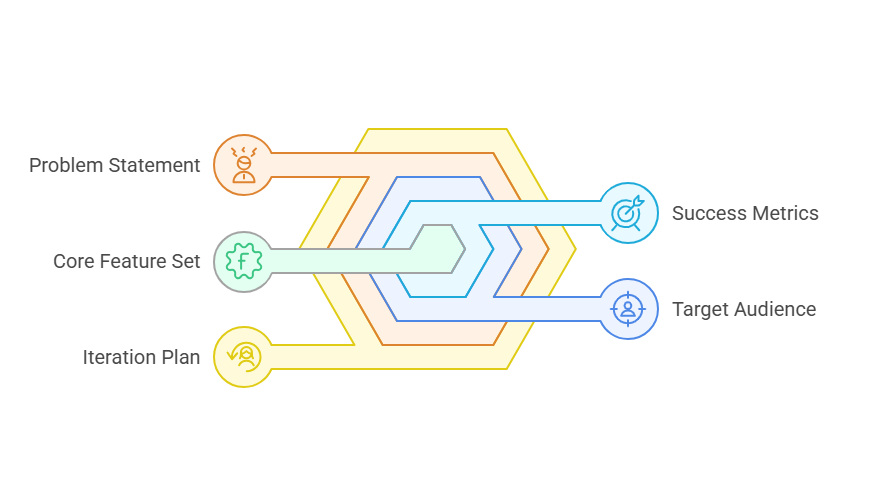
● Problem Statement: Clearly identify the user pain point the MVP addresses.
● Target Audience: Define who the first users will be and why they matter.
● Core Feature Set: List the minimum functions that deliver immediate value.
● Success Metrics: Include quantifiable goals such as adoption, churn reduction, or revenue.
● Iteration Plan: Define how user feedback will be collected and prioritized.
Why It Matters
A well-structured MVP requirements document prevents overbuilding and keeps teams focused. It also provides investors with proof that the product has a systematic roadmap. For reference, a minimum viable product document example might show a one-page outline with a problem statement, three core features, and measurable KPIs tied to user engagement.
Risks and Challenges of MVP Software Development
MVP Software Development is powerful, but it comes with challenges. Startups often stumble when they overlook these common risks:
● Overbuilding too early: Teams add non-essential features, slowing launch and raising costs.
● Weak feedback interpretation: If user input isn’t structured, iteration loses focus.
● Scalability blind spots: MVPs that ignore long-term architecture face costly rewrites later.
● User trust issues: A poorly tested MVP damages credibility faster than a delayed launch.
The takeaway: MVPs succeed when teams embrace speed without ignoring discipline. Every risk can be reduced by anchoring the build around a clear strategy and measurable goals. It is one of the foremost strategies to consider when launching a SaaS MVP.
Real-World Mistakes to Avoid in MVP Development
Even successful companies make mistakes during MVP Software Development. The difference is whether teams learn early or scale a flawed idea.
Common Mistakes That Derail MVPs
● Building too many features: Products like Juicero failed because early versions tried to be “complete” instead of validating one function.
● Ignoring user feedback: Google Wave launched with advanced features but missed adoption cues, showing that skipping the feedback loop can kill even promising products.
● Failing to prove demand: Quibi spent heavily on production without validating consumer appetite. Their failure underscores why SaaS MVP development requires careful demand testing.
● Weak documentation: Without clear requirements, scope creep and misaligned expectations become inevitable.
The Insight
Most failures come not from poor technology but from weak process discipline. Anchoring your MVP in a minimum viable product document and committing to data-driven iteration reduces these risks significantly.
Industry Best Practices: How to Execute MVP Software Development Today
The MVP software development lifecycle is most effective when guided by structured documentation. An MVP requirements document should always include:
● The problem statement and user pain points.
● Success metrics that track adoption and retention.
● A core feature scope that defines essentials vs. extras.
● An iteration framework tied to user feedback.
In SaaS MVP development, containerized environments make it possible to test multiple feature variations without production risks. QA now blends automated tests for reliability with manual testing for user experience. This balance ensures MVPs launch fast without compromising quality.
Best Tools and Tech Stacks for MVP Software Development in 2025
The right tools accelerate MVP validation. In 2025, the following platforms dominate the MVP software development lifecycle:
● Prototyping and Design: Figma, InVision, Balsamiq — perfect for visualizing workflows before coding.
● No-code / Low-code Platforms: Bubble, Webflow, and Microsoft Power Apps — useful for SaaS MVP development tests.
● Core Development Stacks: React, Node.js, and Kubernetes — flexible enough for scaling MVPs into full products.
● Testing & QA Tools: Cypress for automation, Postman for API testing, and Hotjar for user behavior tracking.
Choosing tools that match your team’s skillset is as important as the MVP requirements document itself. Well-chosen stacks keep MVPs lean while ensuring they scale smoothly when adoption spikes.
Metrics That Matter in the MVP Software Development Lifecycle
MVP success depends on measurable validation, not assumptions. During the MVP software development lifecycle, the right metrics show whether the product is solving the intended problem.
Essential MVP Metrics to Track
● Activation Rate: Percentage of users completing the first key action.
● Retention: DAU/MAU ratio shows how often users return after first use.
● Feature Adoption: Tracks whether the core features in the MVP requirements document are being used as expected.
● Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Ensures user growth is sustainable.
● Lifetime Value (LTV): Measures long-term return against CAC.
● Churn Rate: High churn means poor product-market fit, requiring iteration.
Why These Metrics Matter
By tracking these KPIs, teams in SaaS MVP development validate real product-market fit instead of relying on assumptions. For example, a minimum viable product document might set goals such as “retain 40% of users after 30 days” or “achieve feature adoption above 60%.” These numbers guide iteration and investor conversations.
Sample Timeline: From Idea to MVP Launch
MVP Software Development follows a structured path from concept to market launch. Timelines vary, but most teams can deliver an MVP in 3–6 months.
Typical MVP Timeline
Weeks 1–2: Research & Documentation
● Define the problem and create the MVP requirements document.
● Identify the target user group and establish success metrics.
Weeks 3–6: Design & Prototype
● Use tools like Figma for prototyping.
● Build a clickable demo or no-code test if pursuing SaaS MVP development.
Weeks 7–10: Development & Testing
● Build core features only.
● Run automated QA and small user-group testing.
Weeks 11–12: Launch & Feedback Loop
● Release to early adopters.
● Gather feedback, track retention, and update the minimum viable product document with iteration notes.
Why Timelines Matter
Structured timelines keep MVPs lean while proving value early. Teams that extend builds beyond six months often drift toward traditional product cycles, losing the agility that makes MVPs effective.
The Future of MVP Software Development: Faster, Smarter, Global
The next wave of MVPs will be shaped by technology and global-first thinking.
● AI code assistants cut development time by 25%, handling repetitive tasks.
● Low-code tools make MVPs accessible to non-technical founders.
● Predictive analytics use machine learning to forecast retention drivers.
● Cloud-first delivery allows startups to launch in multiple countries from day one.
The MVP software development lifecycle is evolving from “launch small” to “launch smart, learn fast, and expand globally.”
FAQ about MVP Software Development
What is MVP Software Development in simple terms?
MVP Software Development means creating the smallest functional version of a product that solves a user problem, then testing it in the market to collect feedback and validate demand.
How long does the MVP software development lifecycle usually take?
The MVP lifecycle typically lasts 3 to 6 months. Timelines vary depending on complexity, industry requirements, and whether teams use no-code prototypes or custom SaaS MVP development.
What is an MVP requirements document and why is it important?
An MVP requirements document defines the problem, success metrics, and core features. It ensures stakeholders align on priorities and prevents scope creep during the MVP software development lifecycle.
How does SaaS MVP development differ from mobile app MVP development?
SaaS MVP development focuses on cloud scalability, API integrations, and subscription models. Mobile MVPs emphasize platform compatibility, lightweight performance, and device-specific features. Both rely on feedback loops.
What is an example of a minimum viable product document?
A minimum viable product document example usually contains a problem statement, target audience, feature list, timeline, and iteration plan. This ensures MVPs launch with structure and evolve through real-world data.
MVP Software Development as the New Competitive Edge
MVP Software Development doubles startup success rates and drives cost efficiency. Companies like Notion, Discord, Slack, Figma, and Obsidian prove that imperfect but functional launches, refined through feedback, consistently outperform traditional builds.
At EnactOn, we’ve seen this proven across 350+ projects. The winners are the teams that balance speed with quality, simplicity with depth, and vision with validation. That balance is the competitive edge MVPs provide.
